ACPS is taking additional measures to increase awareness of cyber threats at work, and in turn safeguard your personal and professional data. One of the most common threats are from phishing scams that are sent through email.
What are phishing scams?
Phishing scams typically consist of emails that seem harmless but are actually intended to trick users into sharing sensitive information. This is often accomplished by encouraging the user to click on a malicious link or attachment. Phishing emails get their name because the hackers are “fishing” for your personal information.
Most phishing emails appear completely legitimate, often by imitating a company’s logo using high-quality graphics and including opt-out instructions. For this reason, it’s quite common for recipients to be fooled, and even large companies have fallen prey to these scams.
But if you look closely, you can spot the telltale signs.
Common Phishing Trends and Techniques
There are many different techniques perpetrators use to launch a phishing attack. A few of the most common ones are provided below:
- Invoice phishing: Invoice phishing scam emails claim the recipient has an outstanding invoice from a well-known company, bank or vendor. The email instructs the recipient to click on a link to pay their invoice. But when they click on the link and access the site, the hackers steal their personal information and gain access to their bank accounts.
- The virus or compromised account: Viruses and compromised accounts cause users to receive an email from a third party company claiming one of their accounts has been compromised. The email instructs them to log in to reset their password or to download a form, fill in their personal information, and return it. However, a legitimate company would never request your personal information through email in this manner.
- Payment and delivery scam: This tactic involves sending emails from what appears to be a legitimate vendor asking for a user’s credit card information. They typically claim that your payment information needs to be updated before they will deliver your order. Be very careful with these emails, especially if you haven’t purchased anything from the vendor.
- Downloads: Download scams send an email instructing recipients to click on a link. These emails often contain hyperlinks that could download a malicious file onto the end user’s computer. Never click on an email link unless you are absolutely sure that the sender is who they claim to be.
Tips for Spotting Phishing Emails
Although phishing emails often mimic actual companies and vendors, there are ways to detect them. All employees should be aware of the following red flags that indicate a possible phishing email:
- The email contains links or URLs that direct you to the wrong website or try to get you to access a third-party site that is separate from the email sender.
- You receive an email requesting sensitive information such as your social security number, bank account information, or credit card numbers. Consider these emails suspect and never share your personal information without checking with the company first.
- You receive an email requesting your account information such as your network login or email account password. Consider these emails suspect and never share your personal information without checking with the company first.
- You find an unexpected email in your inbox from a person, vendor, or company that you rarely or never deal with. If this happens, the safest thing to do is delete the email without opening it, as there’s a good chance it’s a phishing email.
- The email has obvious errors like typos, poor grammar, or incorrect information. A legitimate email from a company is very unlikely to have these kinds of errors.
- The email address of the sender is incorrect, although it is close to the actual email address. This is another common sign of a phishing email.
Take a look at these two examples of phishing emails:
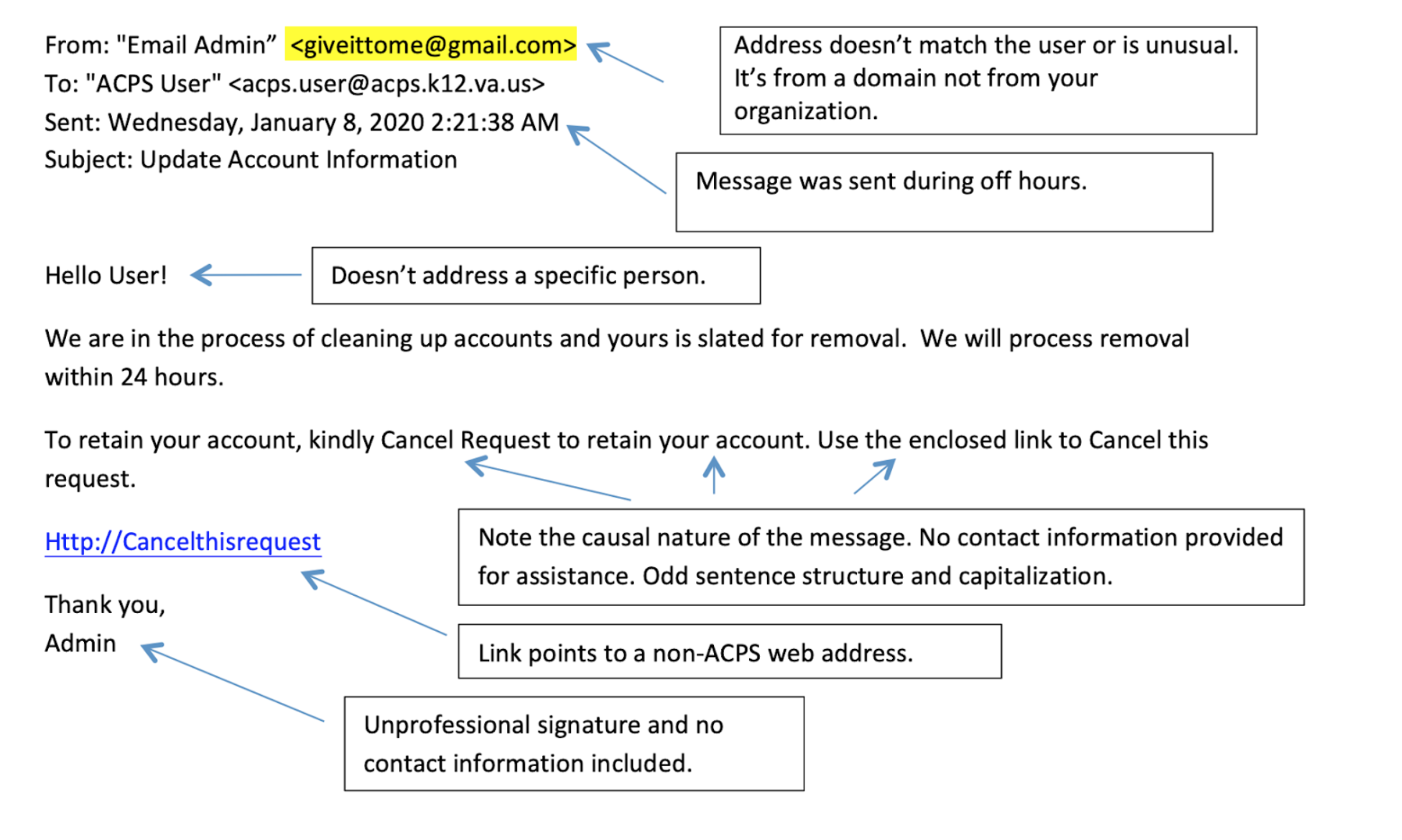

Phishing scams remain a very common type of cyber crime, and can cause major financial losses to individual users and companies.
They are much more sophisticated these days, making them harder to detect. Familiarize yourself with the techniques. By doing so, you can help protect your organization from financial losses and other serious consequences of phishing.

